Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms
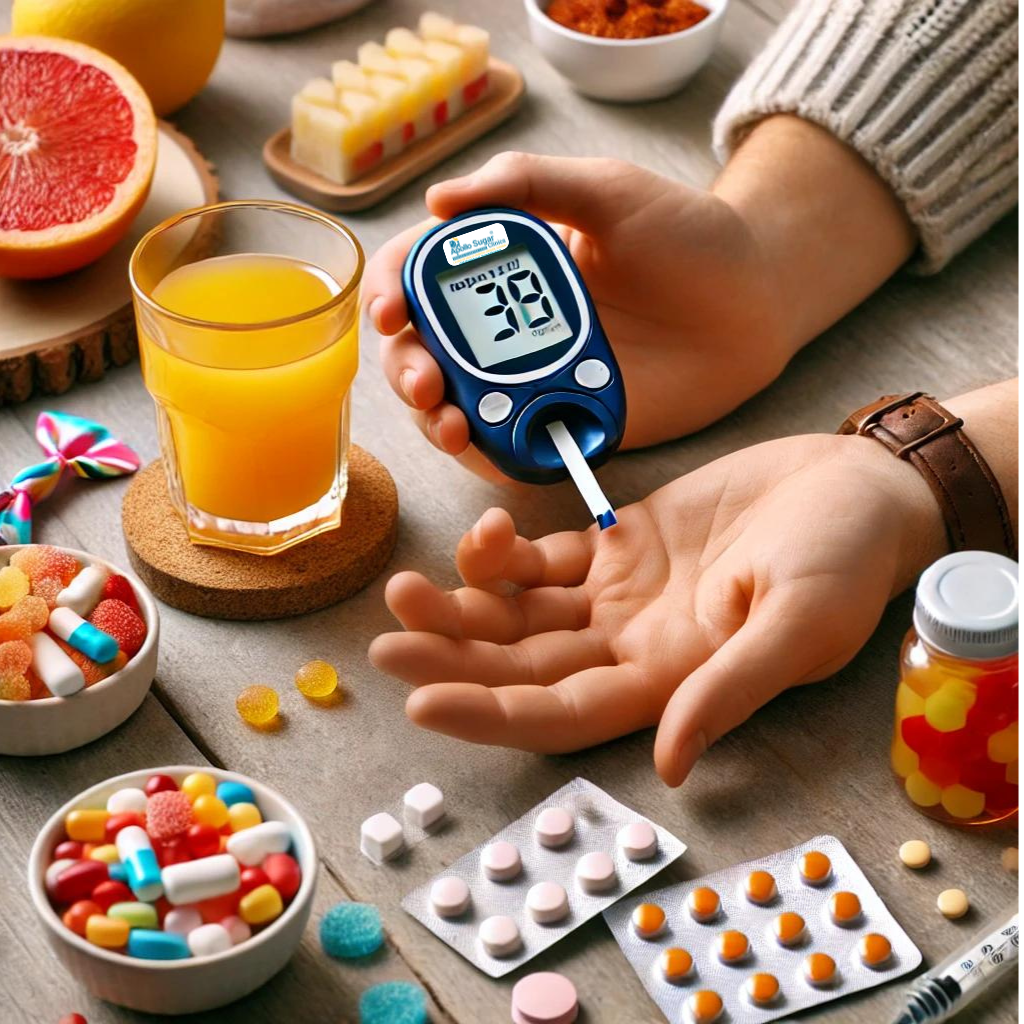
Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms Everything You Need to Know About Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms Introduction Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Recognizing its symptoms early can help in managing and treating the condition effectively. What Is Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Insulin is crucial for allowing glucose to enter cells and produce energy. Without sufficient insulin, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels. Common Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes Understanding the symptoms of Type 1 diabetes is essential for early diagnosis and management. Here are some common signs to look out for: Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination: High blood sugar levels cause excess sugar to be excreted in urine, drawing more water out of tissues and leading to dehydration and increased thirst. Extreme Hunger: Without enough insulin, sugar cannot enter cells to provide energy, leading to constant hunger. Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite eating more, individuals with Type 1 diabetes may lose weight as the body uses muscle and fat for energy due to insufficient insulin. Fatigue: Lack of insulin means glucose isn’t converted into energy effectively, causing persistent tiredness. Blurred Vision: High blood sugar levels can cause fluid to be pulled from the lenses of the eyes, affecting vision. Slow-Healing Sores or Frequent Infections: Type 1 diabetes can impair the body’s ability to heal and fight infections. Additional Symptoms to Watch For While the above symptoms are more common, other signs may indicate the onset of Type 1 diabetes: Irritability or Mood Changes: Blood sugar fluctuations can affect mood and cause irritability. Fruity-Scented Breath: When the body resorts to burning fat for energy, it produces ketones, which can cause a fruity odor in breath. Nausea and Vomiting: Elevated blood sugar levels can trigger nausea and vomiting. Managing Type 1 Diabetes Managing Type 1 diabetes requires a comprehensive approach: Insulin Therapy: Insulin must be taken regularly to maintain blood sugar levels. Blood Sugar Monitoring: Frequent blood sugar testing is crucial to ensure levels stay within the target range. Healthy Eating: A balanced diet helps manage blood sugar levels and supports overall health. Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Conclusion Recognizing the symptoms of Type 1 diabetes early can make a significant difference in management and treatment. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and care. F.A.Q What is Type 1 diabetes? Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to high blood sugar levels. What causes Type 1 diabetes? The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to involve genetic and environmental factors that trigger the immune system to attack the pancreas. What are the common symptoms of Type 1 diabetes? Increased thirst Frequent urination Extreme hunger Unexplained weight loss Fatigue Blurred vision Slow-healing sores or frequent infections How is Type 1 diabetes diagnosed? Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests that measure blood sugar levels and the presence of autoantibodies. Can Type 1 diabetes be prevented? Currently, there is no known way to prevent Type 1 diabetes, but early detection and management can help control the condition. How is Type 1 diabetes managed? Insulin Therapy: Regular insulin injections or an insulin pump. Blood Sugar Monitoring: Frequent testing of blood sugar levels. Healthy Diet: A balanced diet with controlled carbohydrate intake. Exercise: Regular physical activity to help lower blood sugar levels.